
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.
Introduction <br> <br> a certain machine parts manufacturing process using a hard material. These include some high-hardness brittle materials. In this machining field, superhard tools can make a big difference.
In addition to natural diamonds, artificial diamonds have been more widely used in recent years. Synthetic diamond is made of graphite as raw material, adding catalyst, and making single crystal diamond powder through high temperature and high pressure. Can be used as an abrasive. The diamond fine powder is then added to the binder, and after another high temperature and high pressure process, a polycrystalline diamond blade or other product can be produced. Use a similar process. A diamond composite blade (PCD) made of cemented carbide as a base can also be produced. Another recent method is to apply a diamond film (thickness of about 10 μm to 25 μm) on a cemented carbide or ceramic blade by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to form a diamond coated blade (CD). . Or a thick diamond film with a thickness of 0.4 mm or more is deposited first, and then welded to the cemented carbide substrate to form a diamond thick film blade (TFD). CD and TFD are developing technologies, but they are very promising.
Taking hexagonal boron chloride (HBN) as raw material, using the same high temperature and high pressure process as above. It can be made into a polycrystalline cubic boron nitride (CBN) blade or a CBN composite blade.
Second, the crystalline structure of diamond and cubic boron nitride tool of the tool performance <br> <br> diamond and CBN are face-centered cubic, highly abrasion resistance. The hardness of synthetic diamond can reach HV8000~9000, and the hardness of CBN can reach HV6000~7000. Both have a density of about 0.5 g/cm3, which is similar to the density of Al203 and Si3N4.
Their thermal conductivity is very good. The thermal conductivity of diamond is 2000W/(m·K), and the CBN is 1300W/(m·K), which is 5 times and 3.2 times that of copper. They are 40 times and 25 times, respectively, of cemented carbide.
Their linear expansion coefficients are small, diamond is (O.9~1.18)×1O-6/K, and CBN is (2.1~2.3)×1O-6/K, which are 1/6 and 1 of the hard box. /3.
Their modulus of elasticity is very high, with diamonds (850-900) GPa and CBN 720 GPa, which is significantly higher than hard kitchen boxes and ceramics.
During the cutting process, the coefficient of friction between the diamond and CBN tool and the workpiece material is small, about 0.1 and 0.3, which is 1/5 and 1/2 of the cemented carbide tool.
Diamond and CBN tools can be used to sharpen sharp cutting edges, especially natural diamond tools that have been carefully sharpened and ground to achieve a blunt radius of less than a micron.
There is a great inertness between CBN and iron group elements, and no significant chemical action occurs at 1300 ° C; it is stable to acid and alkali. Diamond is prone to chemical reaction to iron group elements. At 700 °C or above, diamond is converted to graphite under the action of Fe element and loses hardness. The C element in diamond is also easy to diffuse to the iron workpiece material. Diamond is also not etched by acid.
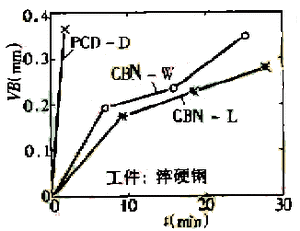 Figure 1 Superhard tool turning hardened steel |
 Figure 2 Hard boxed, ceramic tool turning hardened steel |
 Figure 3 Superhard tool turning carbide |
Next page
November 11, 2024
Письмо этому поставщику

Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.

Fill in more information so that we can get in touch with you faster
Privacy statement: Your privacy is very important to Us. Our company promises not to disclose your personal information to any external company with out your explicit permission.